The 8-4-4 system of education which started in 1985 is coming to an end to pave way for Kenya’s new 2-6-6-3 (2-6-3-3-3) education curriculum framework.
NOTE: The new system is gradually being rolled out and therefore the old system of education (8-4-4) is still in use from Class 7 (Grade 7) to the University level (As of May 2022).
Why Curriculum reform in Kenya
The vision of the basic education curriculum reforms is to enable every Kenyan to become an engaged, empowered, and ethical citizen. This will be achieved by providing every Kenyan learner with world-class standards in the skills and knowledge that they deserve, and which they need in order to thrive in the 21st century. This shall be accomplished through the provision of excellent teaching, school environments and resources, and a sustainable visionary curriculum that provides every learner with seamless, competency-based high-quality learning that values every learner.
Basic Education Curriculum Framework Pillars
The basic education curriculum framework vision and mission are supported by three important pillars; values, theoretical approaches and guiding principles.
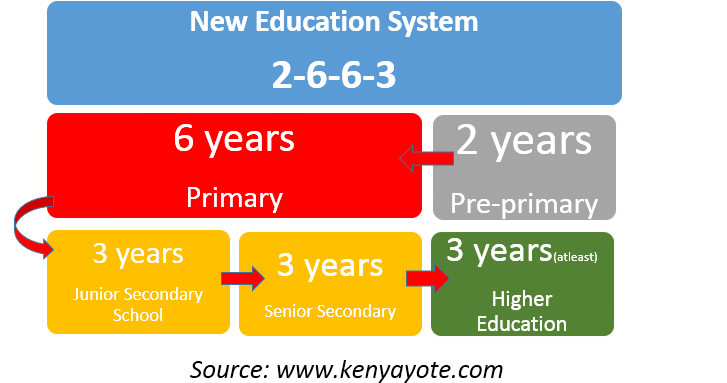
Organization structure of 2-6-6-3 system of education
Basic Education will be organized into three (3) levels: Early Years Education, Middle School Education, and Senior School. The image below presents a summary of the structural model.
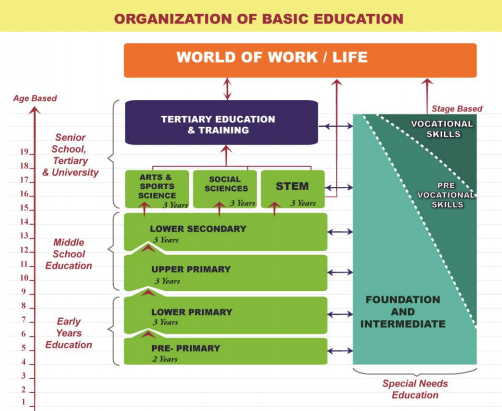
1) Early Years Education (5 years): Pre-primary and Lower primary
This shall comprise two years of pre-primary and three years of lower primary school education
- Pre-primary Education
All learners are expected to begin their education at this level. It is a two-year programme.
Subjects for Pre-primary (Two Years)
- Language Activities
- Mathematical Activities
- Environmental Activities
- Psychomotor and Creative Activities
- Religious Education Activities
NB: Digital literacy and pertinent and contemporary issues will be integrated across all Subjects.
- Lower Primary
The learners from pre-primary 2 will join lower primary in grade 1 at about 6 years of age and spend 3 years in this part of Early Years Education before exiting middle school at the end of grade 3.
The following will be the Subjects in lower primary
- Literacy
- Kiswahili Language Activities/Kenya Sign Language for learners who are deaf
- English Language Activities
- Indigenous Language Activities
- Mathematical Activities
- Environmental Activities
- Hygiene and Nutrition Activities
- Religious Education Activities
- Movement and Creative Activities
NB: ICT will be a learning tool in all areas.
Pertinent and contemporary issues will be mainstreamed in all Subjects.
2). Middle School Education 6 years (upper primary and lower secondary)
This shall comprise three years of upper primary and three years of lower secondary education.
- Upper Primary
Upper primary is part of middle school. It is a three-year programme where learners are exposed to a broad curriculum and given an opportunity for exploration and experimentation.
Subjects for Upper Primary
- English
- Kiswahili or Kenya Sign Language (for learners who are deaf)
- Home Science
- Agriculture
- Science and Technology
- Mathematics
- Religious Education (CRE/IRE/HRE)
- Creative Arts
- Physical and Health Education
- Social Studies
Optional:
11. Foreign Languages (Arabic, French, German, Mandarin)
NB:
ICT will be cross-cutting in all subjects.
Pertinent and contemporary issues and life skills will be mainstreamed in all Subjects.
A pastoral program of instruction will be conducted once a week.
- Lower Secondary
Secondary education is organized into two levels namely, lower secondary (Grades 7, 8, and 9) and senior school (Grades 10, 11, and 12).
Graduates of primary school Grade 6 shall join lower secondary at Grade 7. Lower secondary will expose the learner to a broad-based curriculum to enable them to explore their own abilities, personality, and potential as a basis for choosing subjects according to career paths of interest at the senior school. At Grade 4 learners will be introduced to the optional subjects offered at upper primary so as to make informed choices at Grade 7. Learners in lower secondary will undergo a rigorous career guidance programme and be exposed to the related subjects to enable them to make informed choices as they transition to senior school.
Subjects for Lower Secondary School
The Subjects are in two categories; core and optional subjects. At this level, a broad-based curriculum is offered to enable the learner to explore their own interests and potential as a basis for choosing subjects according to career paths of interest at the senior level.
Core Subjects
Learners will be required to take the 12 core subjects provided.
1. English
2. Kiswahili or Kenyan Sign Language for learners who are deaf
3. Mathematics
4. Integrated Science
5. Health Education
6. Pre-Technical and Pre-Career Education
7. Social Studies
8. Religious Education – learners choose one of the following:
i. Christian Religious Education
ii. Islamic Religious Education
iii. Hindu Religious Education
9. Business Studies
10. Agriculture
11. Life Skills Education
12. Sports and Physical Education
NB: ICT will be a delivery tool for all Subjects.
Optional Subjects
Learners are provided with an opportunity to choose a minimum of one and a maximum of two subjects according to personality, abilities, interests, and career choices from the list provided.
1. Visual Arts
2. Performing Arts
3. Home Science
4. Computer Science
5. Foreign Languages:
i. German
ii. French
iii. Mandarin
iv. Arabic
6. Kenyan Sign Language
7. Indigenous Languages
3). Senior School
Senior School comprises three years of education targeted at learners in the age bracket of 15 to 17 years and lays the foundation for further education and training at the tertiary level and the world of work. It marks the end of Basic Education as defined in the Education Act, 2013.
Learners exiting this level are expected to be “empowered, engaged, and ethical citizens” ready to participate in the socio-economic development of the nation.
The learner entering this level shall have had opportunities at lower secondary to explore their own potential, interests, and personality and is, therefore, ready to begin specialization in a career path of choice. The specialization entails choosing to pursue studies in one of the three pathways available in senior school. He or she can choose the Arts and Sports Science, Social Sciences or Science Technical Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) pathway.
Schools will be specialised institutions that will provide opportunities for learners to focus in a field of their choice as well as form a foundation for further education and training and gaining employable skills. Senior schools will be required to therefore organize open days to enable learners and parents to glean the information necessary for effective decision-making. Additionally, a robust parental empowerment and engagement programme will be necessary to strengthen the involvement of parents in this process.
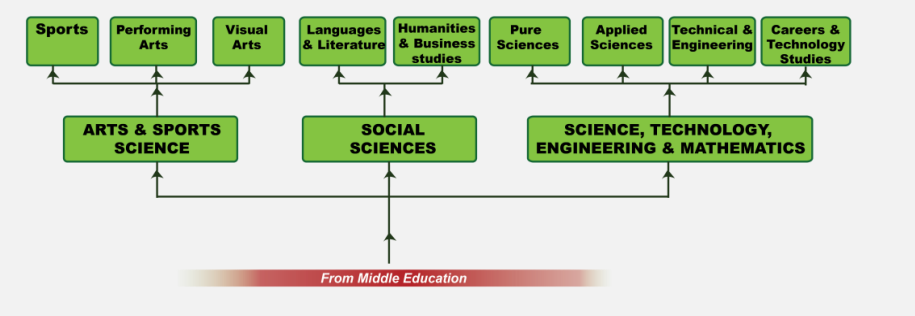
In Kenya, each senior school is expected to make informed decisions with regard to the pathway of choice based on the requisite infrastructure that would ensure the development of the competencies identified in that pathway. The three pathways are: (1) Arts and Sports Science (2) Social Sciences (3) Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM).
Within the three pathways, there are various tracks. Schools can also decide to offer one or more track in the pathway depending on the ability to acquire the infrastructure necessary for the acquisition of the identified competencies.
Education for Learners with Special Educational Needs
Learners with special educational needs, like any other learner, have potential that needs to be nurtured. The special needs education curriculum model illustrated below indicates curriculum provision for learners with special needs.
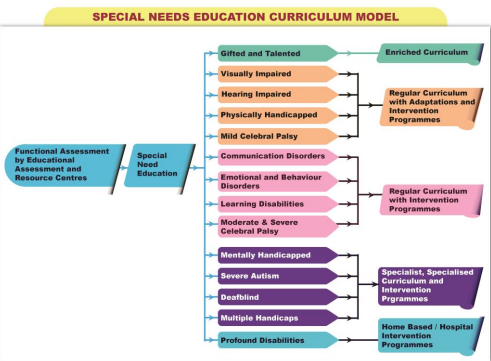
Learners with special educational needs who may follow the regular curriculum may include those with:
- visual Impairment
- Hearing Impairment
- Physical Handicap
- Mild Cerebral Palsy
- Learning Disabilities
- Autism
- Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties
- Communication Disorders and the
- Gifted and Talented
Learners with Special Needs Who May Not have their needs met by just following the Regular Curriculum
Learners with special needs who may not have their needs met by just following the regular curriculum may include those with:
- Mental Handicap
- Deaf blindness
- Severe Autism
- Severe Cerebral Palsy
- Multiple Handicaps
- Profound Disabilities
We hope you have got a basic understanding of the 2-6-6-3 curriculum. We will continue sharing information about Kenya’s new curriculum system. You can also drop us an email for any inquiry.
You might also want to read about CBC assessment and grade transition (explained in detail).
If you are a teacher and need CBC schemes of work, lesson plans, and notes visit: Muthurwa Marketplace.
Do not miss our latest updates on curriculum reports in Kenya and the transition stages up to university.
Leave a Comment